Advantage India
Your next manufacturing destination
India has a distinct advantage with its large internal market, strategic location for exports, and a thriving private sector. This serves India both internally and for the world.
In the new normal, firms are looking to diversify their production bases, and the markets they serve. The objective is to bring in resilience in supply chains. Several global corporations in the automotive, electronics, engineering, food processing, chemicals and healthcare sectors have set up large manufacturing operations in India. The country is emerging as a suitable destination with its:
| Fair Governance |
Quality Infrastructure |
Good Trade and Investment Policy |
Good Regulatory Framework |
Quality Labour |
INDIA AT GLANCE:
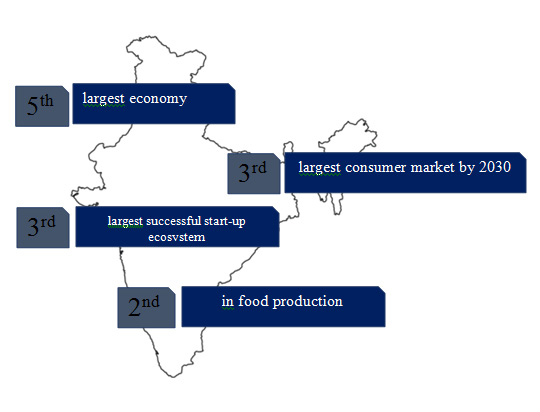
Future perspective
Largest democracy with 910 Million strong electorate
Home to the world’s
largest working age population, estimated to cross 1 billion by 2030
In FY19, India’s total merchandise exports hit a new high of over USD 330 Billion, having registered a 9 per cent growth.
Between FY20 and FY25, commitment of USD 1.5 tn
by Government of India as part of National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), and improvement in energy, transport & logistics, industrial, social and urban infrastructure proposed.
Digital content users expected to grow to 800 Million by 2025.
25 cities in India are among the world’s top 100 fastest growing cities.
India is almost
halfway towards meeting its target of 175 GW of renewable energy by 2022. World’s first country to track performance of each state and union territory on a key performance indicator-driven matrix for their contribution to Sustainable Development Goals
CENTRAL GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
Make in India
- Attracting investments in 25 priority sectors
- USD 357 Billion in FDI since launch in FY2014 till FY20
New sectoral policies
- Production-linked and investment-linked incentives in key sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals and medical devices
Tax reforms
- 17.16% Corporate Tax rate for new manufacturing companies
- Goods & Services tax (GST), implemented from July 1, 2017, subsumed various Indian indirect taxes and helped create a common national market.
High quality industrial infrastructure
- 3,300 parks covering over 1 mn acres of industrial land
- 5 industrial corridors to enable integrated industrial development
Liberal FDI and foreign trade regime
- 100% FDI allowed under automatic route for most manufacturing activities and setting up of manufacturing clusters
- Investments are freely repatriable at fair market value without approvals, subject to payment of taxes
- Import of second-hand goods is generally permitted. Thresholds apply if incentives / low tax rate are to be claimed
STATE GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
Fast-tracking of projects
- States have been hand-holding investors and enabling quick approvals
Fiscal incentives
- Tax-based incentives across sectors and segments of manufacturing
Non-fiscal incentives
- Capital subsidies, discount on tariffs and charges for utilities across various states of India
Customised support for large projects
- Based on the size of investment, customised incentive packages may be availed of
Liberalised labour laws and easier land availability
- States are liberalising labour laws and land parcel processes.
India has improved its ranking from 142 in 2014 to 63 in 2019 in Ease of Doing Business
How India climbed 79 spots in the last 5 years:
Process: Single form for company formation
Time: Fast track approval for construction permits
Trade: ‘Indian Customs Single Window Project’ implemented
Legal: Commercial Courts and Appellate Division of High Courts established
Exit: Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016 for resolving insolvency